Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DME1LQN)
| Drug Name |
Streptomycin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Agrept; Agrimycin; Gerox; Neodiestreptopab; SRY; Strepcen; Streptomicina; Streptomycine; Streptomycinum; Streptomyzin; Liposomal Streptomycin; Streptomicina [Italian]; Streptomycin A; Streptomycin A sulfate; Streptomycin Sesquisulfate Hydrate; Streptomycin sulfate; Streptomycin sulphate; Streptomyzin [German]; Agrept (TN); Estreptomicina [INN-Spanish]; Hokko-mycin; Plantomycin (TN); Rimosidin (TN); Streptomycin & EEP; Streptomycin & Propolis; Streptomycin (INN); Streptomycin (TN); Streptomycin [INN:BAN]; Streptomycin, Sulfate Salt; AS-50 (TN); STREPTOMYCIN SULFATE (2:3) SALT; Agri-mycin-17 (TN); O-2-Deoxy-2-(methylamino)-.alpha.-L-glucopyranosyl-(1->2)-O-5-deoxy-3-C-formyl-.alpha.-L-lyxofuranosyl-(1->4)-N,N'-bis(aminoiminomethyl)-D-streptamine and Liposome; N,N'''-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-4-{5-deoxy-2-O-[2-deoxy-2-(methylamino)-alpha-L-glucopyranosyl]-3-C-formyl-alpha-L-lyxofuranosyloxy}-2,5,6-trihydroxycyclohexane-1,3-diyl]diguanidine; N,N'''-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-4-({5-deoxy-2-O-[2-deoxy-2-(methylamino)-alpha-L-glucopyranosyl]-3-C-formyl-alpha-L-lyxofuranosyl}oxy)-2,5,6-trihydroxycyclohexane-1,3-diyl]diguanidine; 2,4-Diguanidino-3,5,6-trihydroxycyclohexyl 5-deoxy-2-O-(2-deoxy-2-methylamino-alpha-L-glucopyranosyl)-3-C-formyl-beta-L-lyxopentanofuranoside; 2-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-3-(diaminomethylideneamino)-4-[(2R,3R,4R,5S)-3-[(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methylamino)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methyloxolan-2-yl]oxy-2,5,6-trihydroxycyclohexyl]guanidine; 2-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-3-(diaminomethylideneamino)-4-[(2S,3S,4S,5R)-3-[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methylamino)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methyloxolan-2-yl]oxy-2,5,6-trihydroxycyclohexyl]guanidine; 2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3-(diaminomethylideneamino)-4-[(2R,3R,4R,5S)-3-[(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methylamino)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methyloxolan-2-yl]oxy-2,5,6-trihydroxycyclohexyl]guanidine; 2-[(1S,4S)-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)-2-[(2R,5S)-3-[(2S,5R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(methylamino)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4-formyl-4-hydroxy-5-methyloxolan-2-yl]oxy-3,4,6-trihydroxycyclohexyl]guanidine; [2-deoxy-2-(dimethylamino)-alpha-L-glucopyranosyl]-(1->2)-[5-deoxy-3-C-formyl-alpha-L-lyxofuranosyl]-(1->4)-{N',N'''-[(1,3,5/2,4,6)-2,4,5,6-tetrahydroxycyclohexane-1,3-diyl]diguanidine}
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteriaMycobacteriaMycobacterium tuberculosisStaphylococcus aureusEnterococcus faecalisYersinia pestisFrancisella tularensis
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
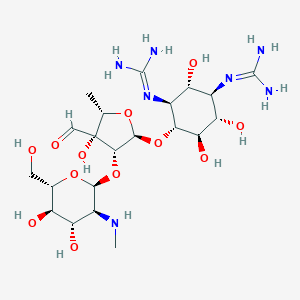 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 4 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 581.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Streptomycin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Streptomycin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
